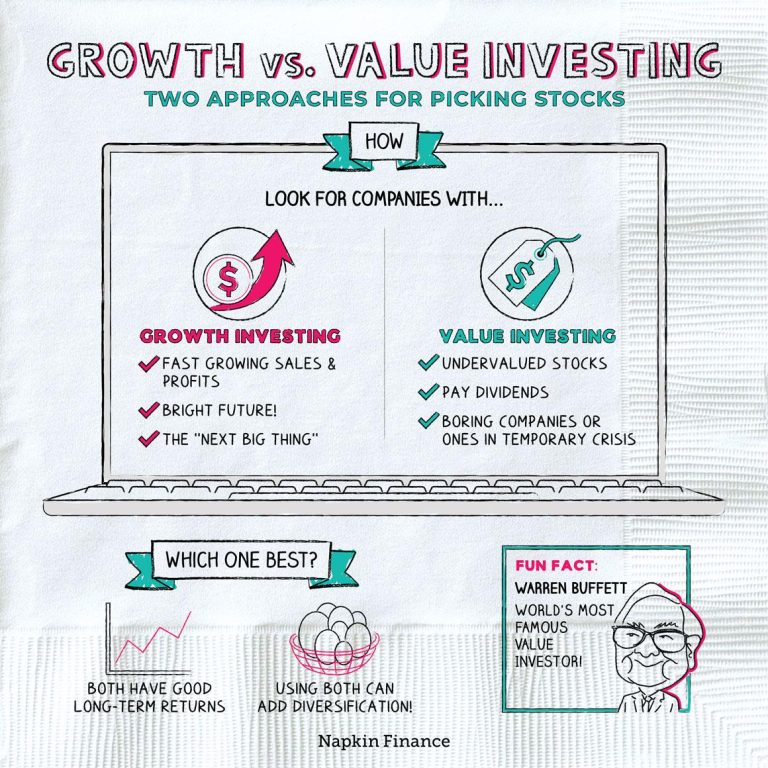
In the world of investing, two strategies often dominate the conversation: growth investing and value investing. Each approach has its ardent supporters and unique methodologies that respond to different market conditions and investor goals. While growth investing focuses on stocks projected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market, value investing seeks out undervalued stocks—those that appear to be trading for less than their intrinsic value.As investors navigate the complexities of financial markets, understanding the fundamental differences between these two strategies is crucial for making informed decisions that align with individual risk tolerance and long-term objectives. In this article, we will delve into the key distinctions between growth and value investing, exploring their philosophies, metrics, and potential benefits to help you determine which approach might be the right fit for your investment journey.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Core Concepts of Growth and Value Investing
- Identifying Key Differences Between Growth and Value Strategies
- Evaluating Risk and Return: What Investors Need to Know
- Practical Tips for Choosing Between Growth and Value Investments
- Closing Remarks
Exploring the Core Concepts of Growth and value Investing
At the heart of growth investing lies the belief that companies will continue to expand at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market. This type of investor typically seeks out firms with robust potential for future earnings, often prioritizing innovation and market disruption. Key characteristics of growth stocks include:
- High Revenue Growth: Consistent increase in sales and profits.
- Competitive Advantage: Strong positioning in emerging sectors.
- Reinvestment: Profits are frequently enough reinvested for further growth, rather than paid out as dividends.
In contrast, value investing focuses on identifying undervalued stocks that trade for less than their intrinsic value. This strategy appeals to investors who believe that the market often misprices the fundamentals of a company, creating opportunities for profit when those prices correct. Characteristics typical of value stocks include:
- Low Price-to-Earnings Ratio: Indicates potential undervaluation.
- Dividend Payments: Often pays dividends, showing underlying financial strength.
- Market Correction Potential: Likely to appreciate once the market recognizes the true value.
Identifying Key Differences Between Growth and Value Strategies
Understanding the nuances between growth and value investing can significantly enhance an investor’s strategy.Growth investing typically focuses on companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry peers. These companies usually reinvest their earnings into the business rather than paying dividends, appealing primarily to investors willing to pay a premium for anticipated future returns.Key characteristics of growth stocks often include:
- High earnings growth potential
- Expensive price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios
- Strong competitive advantages
- Innovation and market expansion capabilities
On the other hand, value investing seeks to identify undervalued stocks that are trading for less than their intrinsic worth. This strategy relies on fundamental analysis, focusing on financial metrics such as dividends, earnings, and assets. Value investors are frequently enough characterized by their patience and long-term outlook, waiting for the market to correct itself. Notable features of value stocks include:
- Low P/E ratios
- Regular dividend payments
- Strong balance sheets
- Market mispricing
Evaluating Risk and Return: What Investors Need to Know
When delving into investment strategies, understanding the risk-return trade-off is crucial.Growth investing often focuses on companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market. This approach can offer substantial returns, but it also comes with heightened risks, especially when businesses fail to meet their aggressive growth projections. In contrast, value investing seeks out stocks that appear undervalued based on fundamental analysis. These investments may not deliver rapid growth,but they often provide a sense of stability,reducing overall portfolio risk.
To effectively evaluate risk and return, investors should consider the following key factors:
- Market volatility: Growth stocks can experience important price swings, while value stocks may provide more consistent performance.
- Time Horizon: growth investing typically requires a longer time frame to realize potential returns, while value investing can yield quicker gains if the stock appreciates to its intrinsic value.
- Dividend Payments: Value stocks often pay dividends, providing a steady return, whereas growth stocks reinvest earnings for expansion.
| Attribute | Growth Investing | Value Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Level | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Duration | Long-term | Short to Medium-term |
| Dividends | Rare | Common |
Practical Tips for Choosing Between Growth and Value Investments
When deciding between growth and value investments, it’s essential to evaluate your risk tolerance and investment horizon. Growth investments are often seen as higher risk, as they rely on the potential for future earnings rather than current valuations. Conversely, value stocks might appeal more to conservative investors looking for stability and income. Consider your financial goals and how long you’re willing to hold your investments. If you’re investing for retirement in a decade or more, growth stocks could offer lucrative returns, whereas value stocks may provide steadier, albeit slower, growth.
To refine your decision-making process,keep the following factors in mind:
- Market Analysis: Regularly review market trends and economic indicators. Growth stocks can be influenced heavily by market sentiment and economic cycles.
- Fundamental Research: Assess earnings reports, sector performance, and company stability. Value stocks frequently enough have lower price-to-earnings ratios but can show solid fundamentals.
- Portfolio Diversification: A balanced approach incorporating both growth and value investments can mitigate risks. Allocate your assets according to your risk profile and investment goals.
Closing Remarks
grasping the distinctions between growth and value investing is essential for any investor aiming to navigate the complexities of the financial markets. Both strategies offer unique advantages and can play different roles within a well-diversified portfolio. Growth investing typically appeals to those seeking high-potential returns, frequently enough accepting higher risks, while value investing attracts individuals looking for stability and long-term gains through undervalued stocks.
Ultimately, the choice between these approaches should align with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. By understanding the nuances of growth and value investing, you can make informed decisions that enhance your investment strategy and, ultimately, work towards achieving your financial objectives.
As you embark on your investment journey, remember that continuous learning and adaptation are key. Stay informed about market trends and be open to adjusting your strategy as necessary. Whether you lean towards growth or value, the most effective investors are those who remain curious, disciplined, and committed to their financial future. Happy investing!