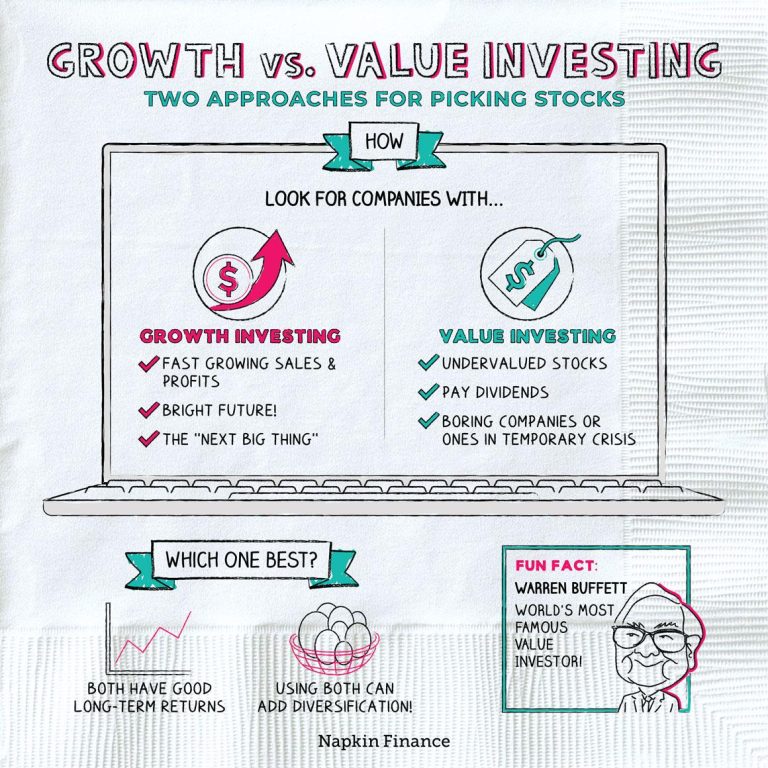
In the ever-evolving world of investing,the debate between growth and value investing remains at the forefront of portfolio management strategies. Both approaches have their staunch advocates and can yield significant returns, yet they embody fundamentally different philosophies about how to identify and capitalize on market opportunities. Growth investing focuses on companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their peers, often prioritizing future potential over current earnings. In contrast, value investing seeks out undervalued companies with strong fundamentals, aiming to profit from the market’s eventual recognition of their true worth. Understanding the key differences between these two investment styles not only equips you to make informed decisions but also helps align your strategy with your financial goals and risk tolerance. in this article, we’ll delve into the core principles behind growth and value investing, explore their unique characteristics, and provide insights into how each can play a distinct role in a well-rounded investment strategy.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Core Principles of Growth and Value Investing
- Analyzing risk and Reward: How Each Strategy Performs in Different Markets
- Identifying Key Metrics: What to Look for in Growth and Value Stocks
- Practical Tips for Investors: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Portfolio
- To Wrap It Up
Understanding the Core Principles of Growth and Value Investing
At the heart of investing strategies lie two distinct philosophies: growth and value investing. Growth investing focuses primarily on companies expected to experience rapid expansion, often sidelining immediate profitability in favor of future potential. Investors lean toward businesses that are innovating or breaking into new markets, typically characterized by high earnings growth rates that may justify higher valuations. Common traits of growth stocks include:
- Strong revenue increases
- High dividend reinvestment rates
- Significant market share advancements
On the other hand, value investing seeks to uncover stocks trading for less than their intrinsic value, often referred to as a bargain. This approach involves rigorous analysis to identify mispriced stocks that demonstrate solid fundamentals and long-term viability. Value investors often favor companies with lower price-to-earnings ratios and attractive dividend yields, checking their potential for recovery over time. Significant indicators of value stocks include:
- Stable earnings history
- Low debt-to-equity ratios
- Consistent dividend payments
| Characteristic | Growth Investing | Value Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Future earnings growth | Current undervaluation |
| Investment Horizon | long-term capital gratitude | Long-term recovery |
| Risk | higher volatility potential | lower volatility, steady performance |
Analyzing Risk and Reward: how Each Strategy Performs in Different Markets
When examining the dynamics of growth and value investing, it’s crucial to understand that each strategy exhibits distinct performance patterns across various market conditions. Growth investing typically thrives in bullish markets where investor sentiment is high, and companies demonstrate strong earnings potential.During these times, growth stocks generally experience significant price appreciation, spurred by innovation and market demand. These stocks frequently enough belong to sectors like technology and biotechnology,which are highly responsive to consumer trends and economic expansion. Conversely, performance can wane during economic downturns, as high-growth expectations may lead to corrections when earnings do not meet projections.
On the other hand, value investing tends to perform well in bearish or volatile markets, where investors seek refuge in fundamentally sound companies that are traded at a discount. this strategy focuses on metrics such as price-to-earnings ratios and dividend yields,identifying opportunities that the broader market may overlook. In such environments, value stocks often exhibit less volatility and foster investor confidence due to their established presence and financial stability. The underlying belief is that these undervalued stocks will eventually appreciate as the market corrects itself. While there may be periods where growth outpaces value,historical trends demonstrate that value investing often yields robust returns during prolonged market corrections.
Identifying Key Metrics: What to Look for in Growth and Value Stocks
When evaluating growth and value stocks, it’s essential to pinpoint specific metrics that can guide your investment decisions. For growth stocks, revenue growth and earnings per share (EPS) are critical. These metrics indicate a company’s ability to generate increasing profits over time. Investors should also examine price-to-earnings growth (PEG) ratio, which provides insight into how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings growth. In addition, operating margin is key, as it reflects how efficiently a company converts sales into actual profit, helping to assess the sustainability of growth.
On the other hand, value stocks often demonstrate different characteristics. The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio is a fundamental metric for identifying undervalued stocks, as it compares a company’s current share price to its earnings per share. Additionally, dividend yield is significant; a higher yield can suggest that a stock is undervalued relative to its cash flow. Investors should also look at the price-to-book (P/B) ratio, which helps to determine if a stock is trading for less than its intrinsic value. Analyzing these metrics allows investors to paint a thorough picture of a company’s financial health and investment potential.
| Metric | Growth Stocks | Value Stocks |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Growth | High and consistent | Typically lower |
| P/E Ratio | Usually high | Generally low |
| PEG Ratio | Less than 1 is ideal | N/A |
| Dividend Yield | Low or none | Higher yields preferred |
| P/B Ratio | N/A | Less than 1 is ideal |
Practical Tips for Investors: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Portfolio
When it comes to investing, selecting the right approach to suit your goals can substantially impact your portfolio’s performance. Growth investing focuses on identifying companies that exhibit potential for substantial earnings or revenue growth. This strategy typically involves investing in younger companies or those in emerging industries, frequently enough at the cost of immediate profitability. Investors who lean towards growth often seek the following characteristics in their selections:
- High revenue growth rates
- Strong market positioning in innovative sectors
- High competitive advantages
- Potential for stock price appreciation despite lower current earnings
On the other hand, value investing centers around finding stocks that are undervalued relative to their intrinsic worth. Value investors look for companies that are trading below their true value consequently of temporary challenges or market misperceptions. Key indicators for this strategy include:
- Low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios
- High dividends or yields
- Strong book value relative to market price
- stable earnings and established business models
To illustrate the differences between these investment strategies, consider the following table:
| Feature | Growth Investing | Value Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Future potential | Current undervaluation |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term capital gains | price correction opportunities |
| Risk level | Higher due to volatility | Lower as value potential provides a cushion |
To Wrap It Up
understanding the fundamental differences between growth and value investing is essential for any investor seeking to build a accomplished portfolio. While growth investing focuses on companies with high potential for expansion and innovation, value investing emphasizes the importance of purchasing undervalued stocks that offer intrinsic worth. Each approach has its own merits and risks, and the best strategy frequently enough lies in finding a balance that aligns with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook.
As you navigate the complexities of the stock market, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research and remain adaptable to changing market conditions. Whether you choose to pursue growth, value, or a hybrid strategy, maintaining a disciplined investment approach and continually educating yourself will empower you to make informed decisions.
We hope this exploration of growth and value investing has provided clarity and insight that enhances your investment journey.Remember, the key to successful investing lies in understanding your personal objectives and harnessing the right tools at your disposal. Happy investing!